Structural stability
Contents [show]
Structural stability is the ability of a structure to maintain its shape and resist deformation or collapse under the action of external loading, e.g. earthquakes, wind, snow and environmental factors, among others. Structural stability is, mainly, known as a field of mechanics that studies the behavior of structures under compression. A structure is referred to as stable if it can retain its equilibrium under the applied loads, and any small perturbation does not cause the structure to fail or collapse.
Structural stability is an important consideration in the design and analysis of structures, particularly those that are subjected to compressive forces. When a structure is subjected to compressive forces, its stiffness may be reduced and its geometry may change, which can cause it to buckle or collapse. To ensure structural stability, engineers use various design and analysis techniques investigating if the structure is capable of resisting the expected loads without collapsing.
Selected Topics
Want to read more like this?
Structural Analysis
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationThe prediction of the response of structures when they are subjected to specified arbitrary extern...
Structural loads
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural loads refer to the forces, pressures, and other external actions that act upon a struct...

AutoFEM Buckling Analysis
Dec, 27, 2013 | SoftwareStructural systems
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationStructural systems refer to the arrangement of structural elements within a building or structure...
Columns
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationColumn, in structural engineering, is a vertical structural element that primarily supports compres...
Structural behavior
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural behavior concerns the way a structure responds to loads, forces, and/or environmental c...

How advanced finite element analysis can prepare buildings for extreme events
Nov, 14, 2024 | NewsWhile most structural analysis software can evaluate everyday stresses, they often fail to prepare...
Damage (structural)
May, 31, 2023 | EducationStructural damage refers to any sudden change, failure or deterioration that occurs within the com...
Continuous structures
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationContinuous structures are also known as continuous systems and refer to a type of structural arran...
Trending

Diaphragms
Structural stability
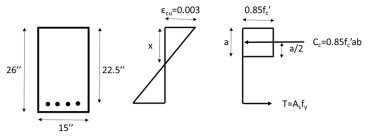
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress
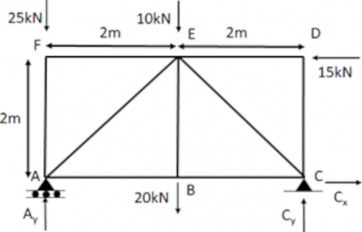
Truss deflection using the unit load method

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculation Example – Beam with inner hinge (Part A). Find the Reactions

