Buckling
Contents [show]
The sudden change in shape of a structural component under a specific loading condition is called bucking in structural engineering. Notable examples are the bowing of a column under compression or the wrinkling of a plate under shear loading. Various modes, depending on the geometry and the loading conditions, are displayed, i.e. lateral, torsional, or global buckling.
When a structure is subjected to a gradually increasing load, and the load reaches a critical level, a member may suddenly change shape and the structure and component is said to have buckled. Euler's critical load and Johnson's parabolic formula are used to determine the buckling stress in slender columns. It should be mentioned that the capacity of a structure against buckling is determined by the structure's material properties, geometry, and/or boundary conditions.
Selected Topics
Want to read more like this?
Structural loads
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural loads refer to the forces, pressures, and other external actions that act upon a struct...
Columns
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationColumn, in structural engineering, is a vertical structural element that primarily supports compres...
Structural stability
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationStructural stability is the ability of a structure to maintain its shape and resist deformation or...

StabLab 2013
Nov, 01, 2013 | SoftwareStructural Analysis
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationThe prediction of the response of structures when they are subjected to specified arbitrary extern...

Sea sponges provide insight into how buildings can resist buckling
Feb, 21, 2017 | NewsBrown University engineers Haneesh Kesari and Michael Monn have been studying sea sponges in order t...

Calculation Example – Buckling of Column (EC3).
Aug, 17, 2016 | EducationCheck the column for buckling according to EC3. HEB300/S275 and axial force NEd=1000KN. The column (...

AutoFEM Buckling Analysis
Dec, 27, 2013 | Software
Types of reinforced concrete structures collapse
May, 20, 2019 | NewsMany types of failure can trigger the collapse of a reinforced concrete building. Any structure m...
Trending

Diaphragms
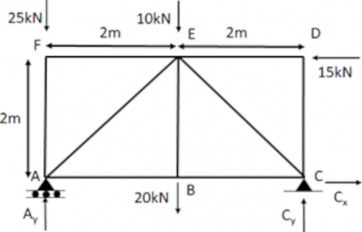
Truss deflection using the unit load method
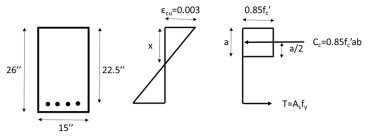
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress

Calculation Example – Plastic Neutral Axis.
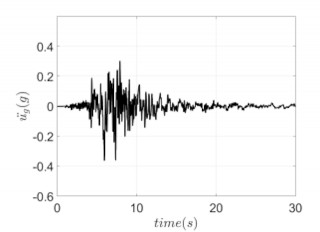
Time History Analysis: process and advantages

