Athens Earthquake, Greece, 7 September 1999
Contents [show]

This page illustrates photos from the Athens, (September 7th, 1999) earthquake, taken by Dimitris P. Zekkos during his reconnaissance the next day of the earthquake. Most photos illustrate typical errors in design and construction of the reinforced concrete structures. Photos of masonry structures are presented also.
Background information about the earthquake
Metamorphosi, while damage was observed on many other suburbs like Peristeri.
One of the most important reasons for the damage was the very small epicentral distance of the city of Athens from the fault. The centre of Athens was approximately less than 10km from the epicenter while the municipality of Ano Liosia was approximately only 2km, Menidi 4km and Metamorphosi 8km. This resulted in high seismic loadings, higher than expected by the older Seimic Codes with which most of the structures were designed. Some directivity effects likely made the situation worse. Recordings at the center of Athens indicated approximately 0.30g while 0.51g was recorded also in one subway station but most likely the response of the instrument is affected by soil-structure interaction. Even though the level of shaking was greater than expected it is illustrated in the photos that follow that in the collapsed structures there were significant design or construction mistakes. Those include:
- Soft-story failures
- Plan-irregularity
- Embedment of architectural elements and utilities inside structural elements.
- Insufficient longitudinal steel reinforcement
- Short column
- Insufficient transverse reinforcement
Checking a structure for serious damage after the earthquake
After the earthquake, the structures that have some fractures need to be checked, to ensure that the structural system is not damaged. The fractures on the masonry walls is not considered as important, since this walls do not take part in the structural system. Attention is paid in fractures where there are columns or beams. In that case, the plaster is removed and the beam or the column is checked. If the fracture does not continue in the concrete then there is no problem.
 |  |
| Failure of Structure because of plan Structural Irregularities | Failure of Structure because of plan Structural Irregularities |
The structure depicted has failed because of plan structural irregularity (SEAOC, table 1-F p.33). Much greater stiffness of the structure in the one corner has caused the rotation of the structure about that corner, and the failure of the other weak columns and beams.
|
|
Bad Structural Techniques
In the first picture you can see a column in order to hide the electrical applications. In the second picture, in the center, you can see a beam. It is obvious that there are not any steel reinforcement. In the third picture, you can see a column. The reinforcement that was installed was basically one rod on the center of the cross-section.
|
|
|
Selected Topics
Want to read more like this?
Columns
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationColumn, in structural engineering, is a vertical structural element that primarily supports compres...
Behavior of Columns During Earthquakes
Jan, 01, 2019 | EducationThe behavior of columns in earthquakes is very important since column failures may lead to additiona...

Types of reinforced concrete structures collapse
May, 20, 2019 | NewsMany types of failure can trigger the collapse of a reinforced concrete building. Any structure m...
Earthquake Engineering
Jan, 01, 2019 | EducationEarthquake engineering is a critical field of civil engineering that focuses on the analysis, desi...

Concrete Component Design Using STAAD.Pro
May, 09, 2022 | NewsSTAAD.Pro structural analysis and design software from Bentley has been widely used for designing...
Structural Analysis
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationThe prediction of the response of structures when they are subjected to specified arbitrary extern...

September 7, 1999: a strong earthquake struck Athens, Greece
Sep, 07, 2023 | NewsOn September 7, 1999, Athens experienced a catastrophic earthquake. The event resulted in the loss...
Beams
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationBeam, in structural engineering, is a horizontal structural element that is designed to carry and...
Structural stability
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationStructural stability is the ability of a structure to maintain its shape and resist deformation or...
Trending

Diaphragms
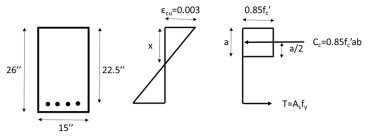
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress
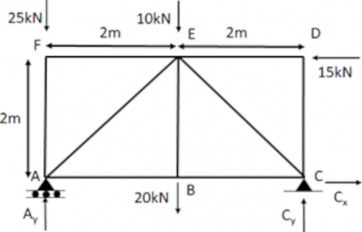
Truss deflection using the unit load method

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculation Example – Beam with inner hinge (Part A). Find the Reactions

Method of sections






