Valdivia Earthquake, Chile, May 22, 1960
Contents [show]
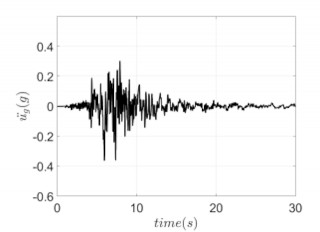
On May 22, 1960, a Mw 9.5 earthquake, the largest earthquake ever instrumentally recorded, occurred in southern Chile. The series of earthquakes that followed ravaged southern Chile and ruptured over a period of days a 1,000 km section of the fault, one of the longest ruptures ever reported. The number of fatalities associated with both the tsunami and the earthquake has been estimated to be between 490 and 5,700. Reportedly there were 3,000 injured, and initially there were 717 missing in Chile. The Chilean government estimated 2,000,000 people were left homeless and 58,622 houses were completely destroyed. Damage (including tsunami damage) was more than $500 million U.S. dollars. The main shock setup a series of seismic sea waves (tsunami) that not only was destructive along the coast of Chile, but which also caused numerous casualties and extensive property damage in Hawaii and Japan, and which was noticeable along shorelines throughout the Pacific Ocean area. There were several other geologic phenomena besides tsunamis associated with this event. Subsidence caused by the earthquake produced local flooding and permanently altered the shorelines of much of the area in Chile impacted by the earthquake. Landslides were common on Chilean hillsides. Cordón Caulle erupted forty-seven hours after the main shock. It is only a matter of time until Chile once again has a "world-class" earthquake whose impact, like the 1960 Chile event, will be felt around the world.
Selected Topics
Want to read more like this?

The five strongest earthquakes ever recorded
Sep, 09, 2023 | NewsThe following lines describe five of the most devastating earthquakes in history: The Great Chile...

11 strongest earthquakes worldwide over the last 2 centuries
Jul, 11, 2024 | NewsIt is estimated that at least 20,000 earthquakes occur every year worldwide due to the movement of...

Earthquakes: five deadliest earthquakes ever recorded around the world
Feb, 24, 2022 | NewsEarthquakes are one of the most dangerous natural disasters. More than 100 earthquakes of the magni...

North Chile: A strong 7.3 magnitude earthquake hit the region last Wednesday
Jul, 17, 2024 | NewsOn Wednesday 17th of July, a massive 7.3 magnitude earthquake shook North Chile according to the Eu...

5.8-magnitude earthquake strikes Ecuador coast: damaged buildings, huge loss of property, no tsunami
Mar, 28, 2022 | NewsA huge loss of property was suffered when an earthquake of magnitude 5.8 struck Ecuador coast on Sa...

6.3-magnitude earthquake struck Central Chile
Mar, 30, 2023 | NewsThe Central Chilean coast was hit by an earthquake of magnitude 6.3 on Thursday, according to the N...

Messina earthquake (1908): a civil engineering landmark
May, 26, 2023 | EducationThe 1908 Messina earthquake, also known as the Great Reggio earthquake, is considered as one of t...

Powerful earthquake hits offshore near Chile and Argentina
May, 02, 2025 | NewsA powerful earthquake with a magnitude of 7.4 struck about 219 kilometers south of Argentina on Fri...

Two powerful earthquakes hit China: Reports of 3 people dead
May, 24, 2021 | NewsTwo separate, strong earthquakes that struck in China have resulted in, at least, 3 fatalities. The...
External Resources
Trending

Diaphragms
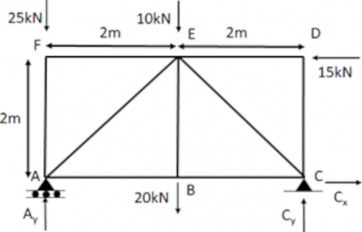
Truss deflection using the unit load method
Structural stability
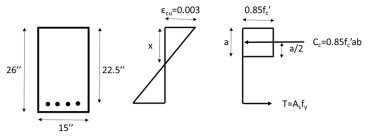
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress

Calculation Example – Plastic Neutral Axis.