Foundations
Foundations are the bedrock of a structure, forming the critical link between the building and the ground. In structural engineering, the foundation is a fundamental component responsible for distributing the structural loads from the building to the supporting soil or bedrock. It serves as the base upon which the entire structure rests, ensuring its stability. Foundations accommodate the unique demands of each building or infrastructure, taking into account factors such as soil conditions, structural loads, and environmental considerations. The two primary types of foundations are shallow foundations and deep foundations. Shallow foundations are situated close to the surface and distribute loads primarily through bearing capacity, while deep foundations are designed to transfer loads to deeper, more stable layers of soil or bedrock when shallow soils are inadequate. Foundations are essential for preventing settlement and structural failure. Their design and construction require expertise in geotechnical engineering to ensure that the foundation can safely support the intended structure and protect it from either adverse soil conditions or external forces.
Want to read more like this?

STAAD Foundation Advanced
Mar, 30, 2022 | Software
Altair S-FOUNDATION
May, 16, 2018 | Software
Bentley Webinar: From Vision to Reality: Leverage STAAD Foundation Advanced's Latest Enhancements
Sep, 11, 2024 | EventAs foundation design becomes more crucial in modern structural analysis and design process, enginee...
Soil structures
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationSoil structures refer to constructions that involve the use of soil as a fundamental building mate...

Bentley Webinar: Solving the Unique Design Challenges of Power Grid Foundations with STAAD Foundation Advanced 2025
Jul, 07, 2025 | EventSubstation and transmission foundations face unique demands—heavy electrical equipment, complex loa...

Bentley Coffee Corner: Structural Asia Pacific - Mastering Plant Foundation Design in STAAD Foundation Advanced
Mar, 15, 2023 | EventThis technical discussion covers the plant foundation module of STAAD Foundation Advanced. Topics w...
Structural loads
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural loads refer to the forces, pressures, and other external actions that act upon a struct...

STAAD Foundation Advanced 2024 (v24.00.01) Release Update
Feb, 07, 2025 | NewsWith the new STAAD Foundation Advanced 2024 (v24.00.01) release users can now design isolated and c...

Power Installed Foundation Anchors offer attractive benefits
Oct, 05, 2016 | NewsOver 90 years of research, development and testing have advanced Chance's Instant Foundation® System...
Trending

Diaphragms
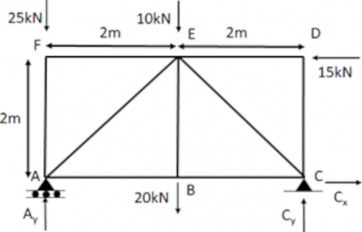
Truss deflection using the unit load method

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress
Structural stability
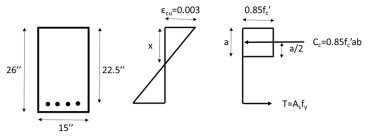
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculation Example – Plastic Neutral Axis.

