Vibration and damping
Vibration refers to a periodic motion of a structure around a reference point that is caused by an external force or a disturbance. In structural engineering, vibration can be caused by several sources that include wind, earthquakes, or traffic, and it can lead to significant damage.
Damping is a technique used to reduce the amplitude and duration of vibrations, by absorbing or dissipating the energy of the oscillations. There are several ways to achieve damping in structures, including viscous damping, structural damping, and tuned mass damping. The technique of viscous damping involves the use of dampers that contain a fluid or a viscous material, such as oil or silicone. In fact, viscous dampers work by converting the kinetic energy of the vibration into heat energy, which is then dissipated. Structural damping involves modifying the structure itself to improve its damping characteristics, by adding mass or stiffness to the structure in specific locations. Structural damping is typically achieved by adding materials with high damping ratios, such as rubber. Tuned mass damping involves adding a mass or a series of masses to a structure at specific locations to alter its natural frequencies and reduce the amplitude of vibrations. The masses are tuned to the frequency of the vibration, which can effectively cancel out the oscillation. By reducing the amplitude and duration of vibrations, damping can help to improve the safety and reliability of these structures.
Want to read more like this?

Depreciation models to accelerate the building construction
May, 23, 2024 | NewsResearch that has been conducted by a team from the University of Bristol and published in the jour...
Structural control
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural control refers to the application of various techniques to mitigate and manage the vibr...
Structural Analysis
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationThe prediction of the response of structures when they are subjected to specified arbitrary extern...

Compos
Aug, 28, 2023 | SoftwareWind engineering
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationWind engineering is a branch of engineering that focuses on studying the effects of wind on various...

Innovative strategies in earthquake-resistant building design: ensuring safety and structural integrity
Jul, 16, 2024 | NewsThe major concern that engineers and architects have when they design a new building is to ensure t...
Structural stability
Sep, 16, 2022 | EducationStructural stability is the ability of a structure to maintain its shape and resist deformation or...
Earthquake Engineering
Jan, 01, 2019 | EducationEarthquake engineering is a critical field of civil engineering that focuses on the analysis, desi...
Dynamic loads
May, 31, 2023 | EducationDynamic loads are loads that vary over time. They can be caused by different factors, such as wind...
Trending

Diaphragms
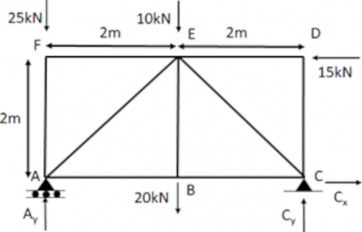
Truss deflection using the unit load method
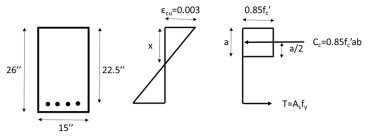
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress

Calculation Example – Plastic Neutral Axis.
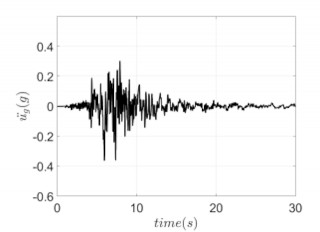
Time History Analysis: process and advantages

