Polymers that function as heat conductors
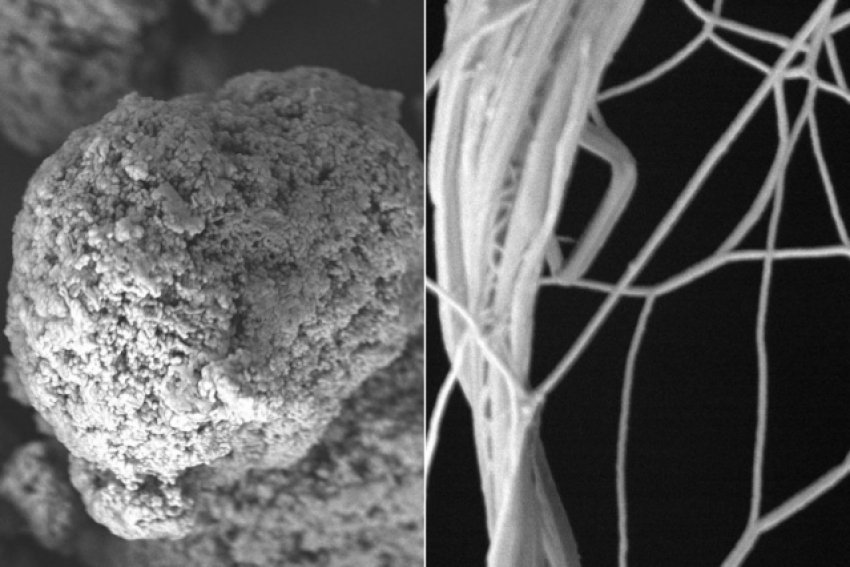
Scientists from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have introduced a new method of producing conductive polymers.
Polymers are materials than are normally used to trap heat while heat conduction is mostly associated with metals. However, for the first time, researchers have managed to produce polymer films (continuous layers of polymers up to 0.2–0.3 mm thick) that act as heat conductors and perform even better than some metals. The study was recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
The findings are of great importance as such polymers can replace common metal conductors in electronic devices such as mobile phones, laptops, computers and in construction industry while being more lightweight, flexible and durable. "Our bigger vision is, these properties of polymers can create new applications and perhaps new industries, and may replace metals as heat exchangers," Gang Chen, senior co-author of the study and the Carl Richard Soderberg Professor of Power Engineering at MIT, stated.
The project comes after the team's successful attempt to produce highly conductive fibers of polyethylene in 2010. Back then, many industrial manufacturers and investors were attracted by the idea but there was a scale issue as the fiber were very thin to be used in common practices. Therefore, researchers had to find a manner to scale up their conductive polymer fibers. "At that time, we said, rather than a single fiber, we can try to make a sheet. It turns out it was a very arduous process," Prof. Chen, stated.
The team managed to produce thin films of conducting polymers beginning with the fabrication of a polyethylene powder. Typically, a polyethylene powder consists of a microscopic structure that includes tangled molecular chains from which heat cannot be transferred easily. This is why polymers are normally insulators. However, the researchers found a technique to untangle those chains increasing the materials' heat conduction by 60-120 times making it even more conductive than steel and ceramics.
In the future, the scientific crew will look into how to optimize the procedure of transforming polymers into heat conductors by investigating on the fabrication technique and on the utilization of different kind of polymers.
Source: MIT.edu
Want to read more like this story?

Improving concrete's fire resistance with tire fibers
Feb, 28, 2019 | NewsIn a new study, researchers have developed a method to improve concrete's performance when subjected...

Bio-inspired composite cement: a new material to increase durability using natural principles
Jun, 28, 2024 | NewsPrinceton’s university engineers developed a new composite cement inspired by oyster and abalone sh...

Strengthening and repairing concrete structures using paper-thin carbon fiber reinforced polymers
Apr, 07, 2021 | NewsA new method to strengthen and repair deficient bridges with paper-thin material has been recogni...

How long can fiber reinforced polymer sustain concrete structures? A question that is answered by scientists
Oct, 14, 2021 | NewsIt is a fact that, in modern society, the majority of our infrastructure (buildings, bridges, tunne...

EPFL scientists develop hydrogel-based 3D printing that yields metals 20× stronger
Oct, 16, 2025 | NewsResearchers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne(EPFL) have developed an innovative addi...

10 state-of-the-art sustainable materials that will alter construction industry
Jun, 10, 2024 | NewsIn 2024, sustainable materials become state-of-the-art in construction since the construction indus...
Metal structures
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationMetal structures refer to constructions primarily built using metal as the fundamental building ma...
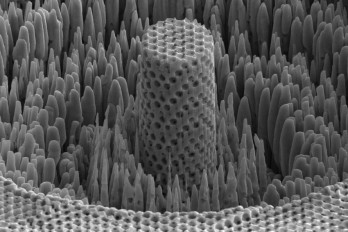
New lightweight material has the strength of titanium
Feb, 22, 2019 | NewsResearchers have developed a sheet of nickel with nanoscale pores that has the strength of titanium...
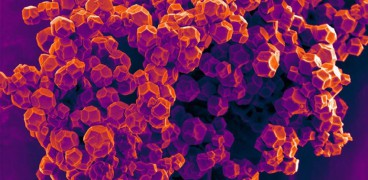
Predicting the mechanical properties of metal-organic frameworks using Machine Learning
Jun, 13, 2019 | NewsA new study suggests that machine learning can predict the mechanical properties of metal-organic fr...
Trending

New Release - STAAD.Pro 2025

Melbourne Approves Skinny Skyscraper

Spectacular interchanges around the world

Maine Medical Center

Buildings Prone to Earthquakes

Roof collapse at Curragh Coal Mine leaves one worker missing


