Shells
A shell refers to a thin, curved, and continuous structural element that forms a three-dimensional surface. When both strength and aesthetics are crucial, shells are notable for their ability to distribute loads through their surfaces, making them ideal for several applications. Shells are widely used in architecture and engineering to create iconic buildings and structures with complex, organic shapes. Shells come in various forms, including domes and vaults, while shells with single or double curvature are commonly used. The efficiency of shells in load distribution allows for the creation of large, open spaces with minimal interior supports or columns. The design and analysis of shell structures involve sophisticated engineering principles, as they must account for factors such as material properties, geometry, and loading conditions.
Want to read more like this?
Domes (structure)
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationDomes are iconic architectural and structural elements known for their elegant and curved shapes th...
Thin wall structures
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationThin wall structures are constructions characterized by their minimal thickness in relation to thei...

Massive concrete umbrellas to be used as a coastal shield
Apr, 02, 2020 | NewsScientists from the University of Princeton in New Jersey, have introduced a radical structural sys...
Structural loads
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationStructural loads refer to the forces, pressures, and other external actions that act upon a struct...

ADINA 2024 New Release!
Sep, 06, 2024 | NewsProduct versioning for Bentley Systems is now based on the calendar year of the major release accor...

A new resource-efficient way to construct a concrete dome has been developed
Mar, 02, 2017 | NewsResearchers at TU Wien have developed a construction method for concrete domes, requiring far less a...
Decks
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationDecks refer to horizontal platforms or structural elements that serve various purposes within a str...
Columns
Sep, 14, 2023 | EducationColumn, in structural engineering, is a vertical structural element that primarily supports compres...
Continuous structures
Sep, 07, 2023 | EducationContinuous structures are also known as continuous systems and refer to a type of structural arran...
Trending

Diaphragms
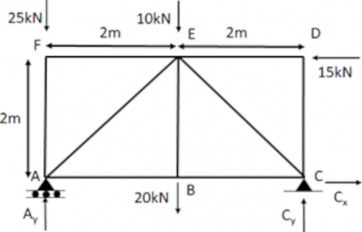
Truss deflection using the unit load method
Structural stability
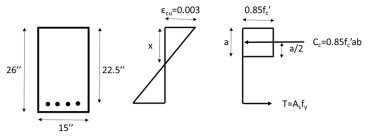
Nominal flexural strength of a reinforced concrete beam

Overhanging beam: shear force and bending moment calculation

Calculate the Maximum Shear Stress

Calculation Example – Plastic Neutral Axis.